cache策略
cache层级与更新策略概览
"There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things." - Phil Karlton
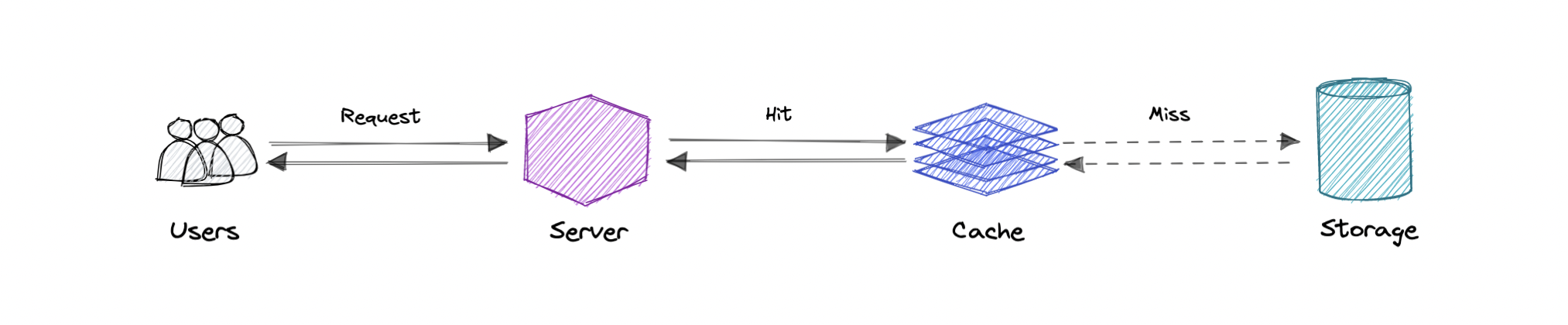
Cache 的核心目的,是通过减少对底层慢存储的访问来提升 data retrieval performance。用容量换速度,cache 通常只存一小部分数据而且是 transient 的;而 database 的数据一般是完整且 durable 的。
Cache 利用了 reference locality 的原则:"最近被请求的数据,很可能会再次被请求"。
Caching and Memory
像计算机内存一样,cache 是一种 compact 且 fast 的 memory,按层级组织,从 L1 到 L2、L3 逐级扩展。cache 也会被写入,例如数据更新后需要写入 cache,替换旧内容。
无论读还是写,cache 都是以 block 为单位。每个 block 都会有一个 tag,记录它在 cache 中的 location。当请求到来时,系统会先在 L1 的 tags 中查找目标内容;如果没找到,就继续查 L2、L3 直到找到为止。找到了就读并加载;如果完全没找到,就写入 cache 以便下次更快命中。
Cache hit and Cache miss
Cache hit
Cache hit 指内容成功从 cache 返回。系统快速扫描 tags,当数据被找到并读取,就算 cache hit。
Cold / Warm / Hot Cache
Cache hit 还会按读取速度分为 cold、warm、hot。
- Hot cache:数据从 L1 命中,读取速度最快。
- Cold cache:命中但在更低层(如 L3 或更低),速度最慢,但仍是 hit。
- Warm cache:介于 hot 与 cold 之间,通常是 L2 或 L3。
Cache miss
Cache miss 指在 cache 中没找到数据,这时系统会去后端取数据并写入 cache。
Cache Invalidation
Cache invalidation 是把 cache 条目标记为无效并移除或替换的过程。当数据被修改时,必须同步 invalidation,否则可能导致应用行为不一致。常见策略有三类:
Write-through cache
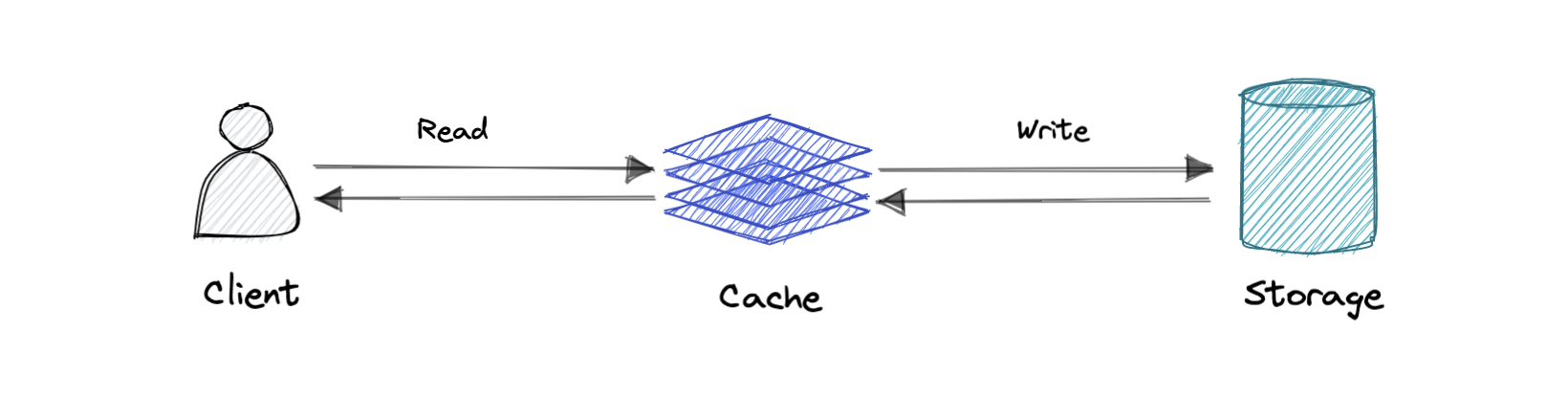
数据写入 cache 的同时,也写入对应的 database。
Pro:读非常快,cache 与存储一致性强。
Con:写入 latency 更高。
Write-around cache
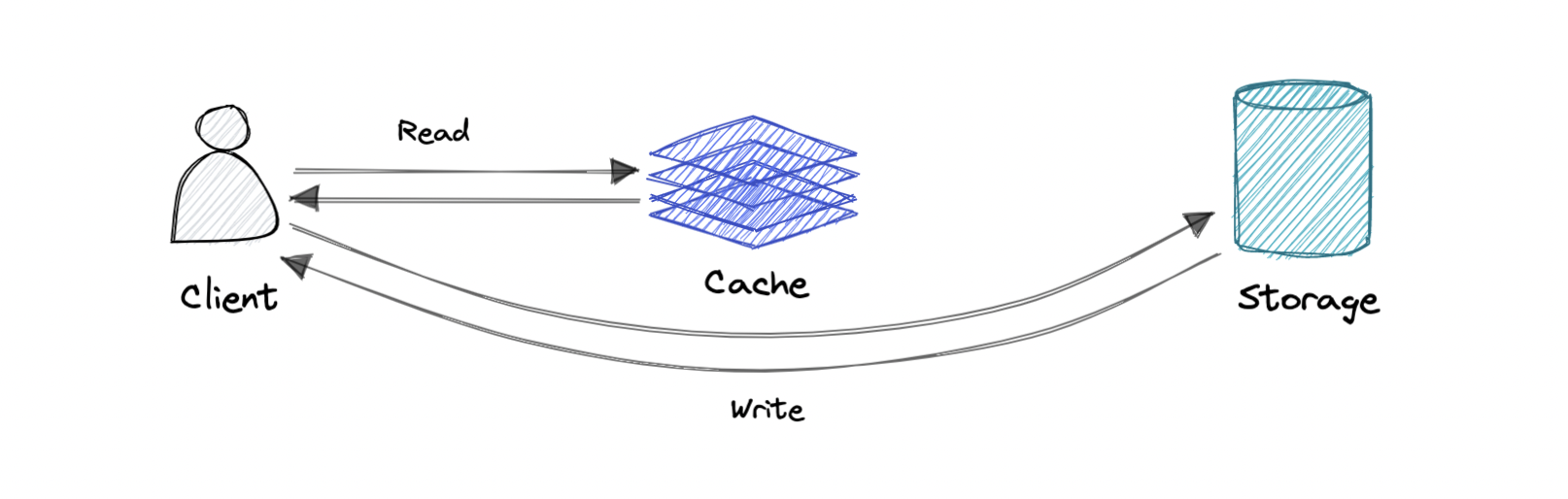
Write 直接落到 database 或 persistent storage,绕过 cache。
Pro:写入 latency 低。
Con:cache miss 变多。miss 时只能去 database 读取,导致读 latency 增高,尤其是“写完马上再读”的场景。
Write-back cache
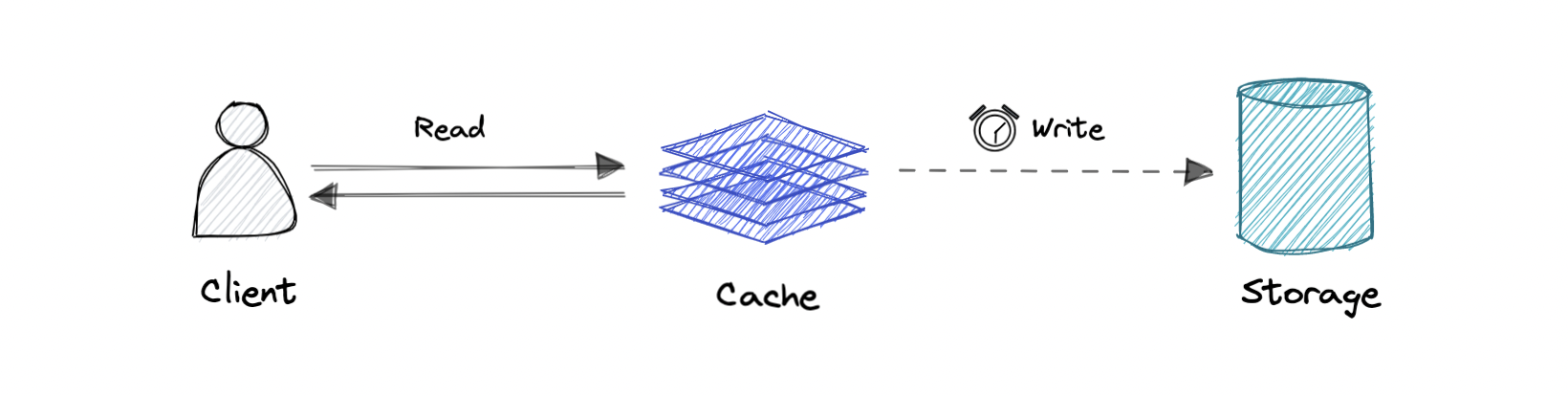
写只落到 cache,写入完成即返回成功;cache 再异步把数据同步到 database。
Pro:写 latency 更低,write-heavy 场景吞吐更高。
Con:如果 cache 层崩溃可能丢数据。可以通过多副本确认写入来降低风险。
Eviction policies
常见 cache eviction policies:
- First In First Out (FIFO):最早进入的 block 最先被淘汰。
- Last In First Out (LIFO):最近进入的 block 最先被淘汰。
- Least Recently Used (LRU):淘汰最久未使用的 item。
- Most Recently Used (MRU):与 LRU 相反,淘汰最近使用的 item。
- Least Frequently Used (LFU):统计使用频率,最少使用的先淘汰。
- Random Replacement (RR):随机选一个淘汰。
Distributed Cache
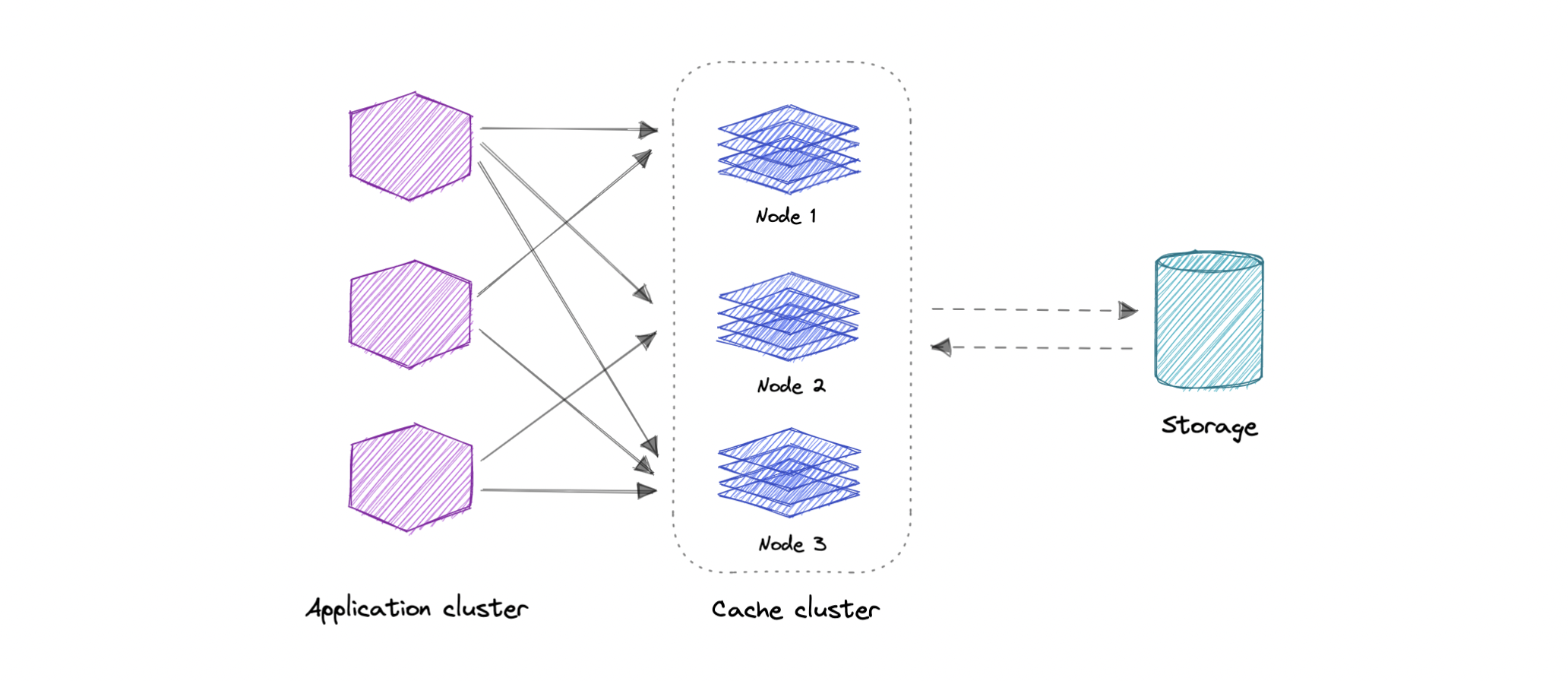
Distributed cache 会把多台机器的 RAM 聚合成一个 in-memory data store 用作 cache。传统 cache 只在单机内存里,而 distributed cache 通过多机组合突破单机内存上限。
Global Cache
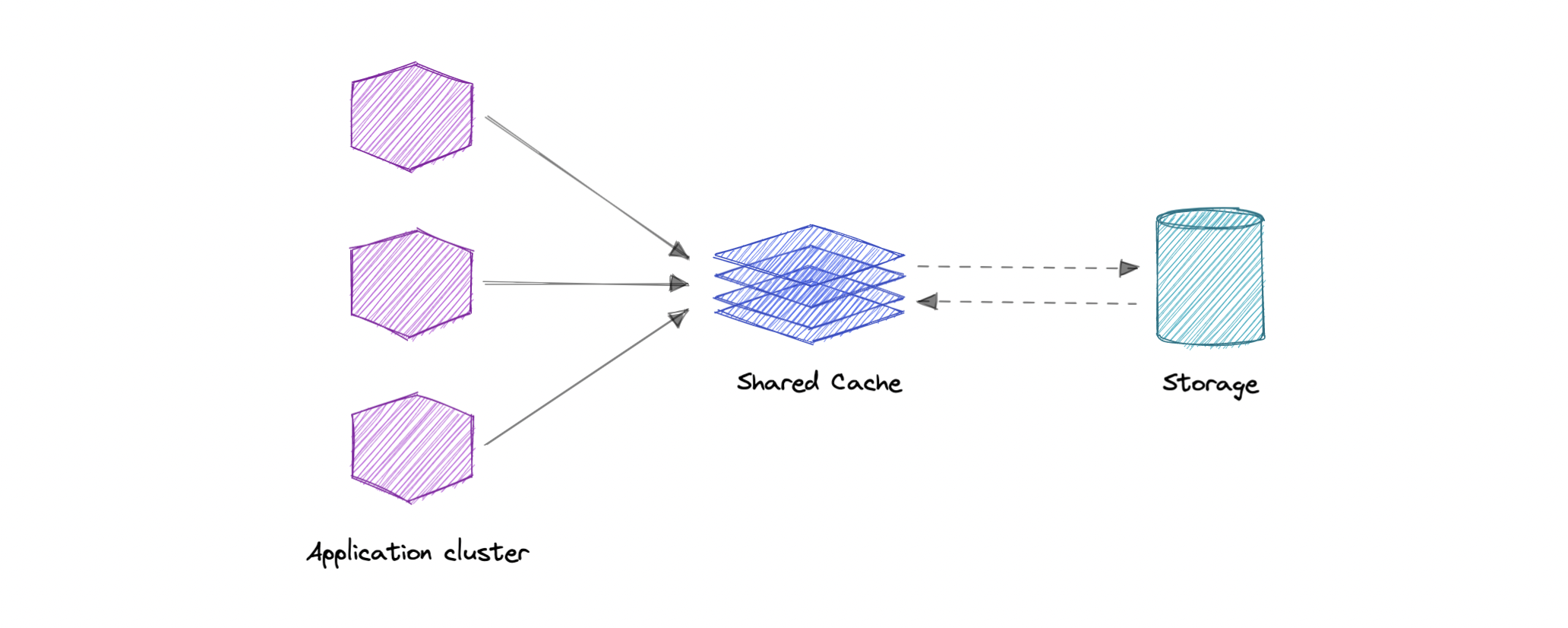
Global cache 是所有 application nodes 共享的 single cache。请求命中失败时,cache 负责去底层数据存储拿缺失数据。
Use cases
Cache 的常见场景:
- Database caching
- CDN
- DNS caching
- API caching
什么时候不适合用 cache?
- 访问 cache 和访问主存储耗时差不多,收益不大。
- 请求重复率低、随机性高,cache hit 率很差。
- 数据变化频繁,cache 容易过期导致每次都要回源。
需要强调:cache 不应该作为永久存储。它几乎总是基于 volatile memory,实现速度快但数据是 transient 的。
优点
- 提升 performance
- 降低 latency
- 降低 database 负载
- 降低网络成本
- 提升 read throughput